This article deals with the following topics: - What are data point strategies?
- A list of all strategies
- Example: calculating the summ of child facilities
1. What are data point strategies?Every facility data point has a strategy that collects data from source time various external and internal sources series to process them. A data point receives its data, depending on the strategy, either from external time series, another data point or more than one data point. Therefore, a facility data point always needs a strategy to find data and process it according to its specific requirements.
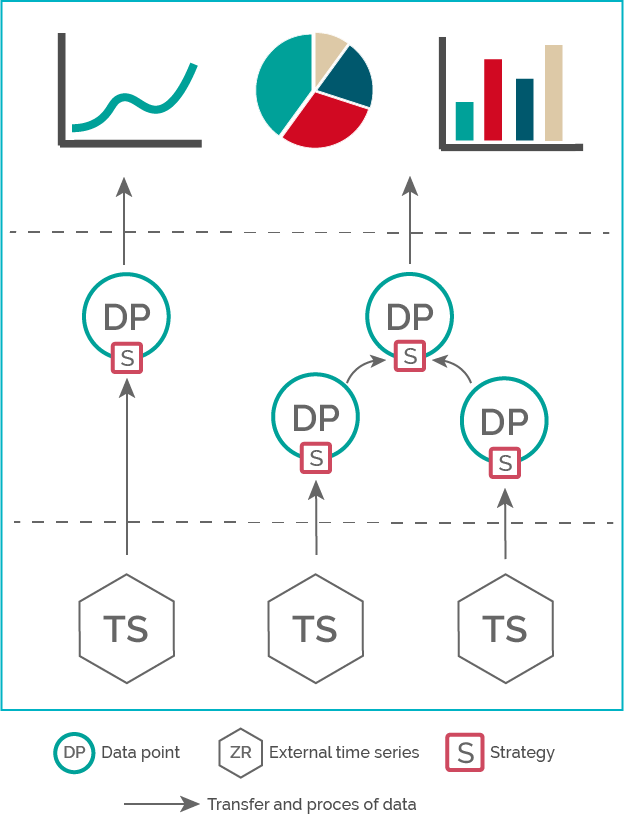
2. A list of all strategiesVarious strategies are available for you in QBRX, which are all grouped up by their respective source time series. At the left side of the table, you can see the source and the matching strategy. The following columns deal with the possible configurations of the targeted time series. The Description gives additional information about the strategy. | Source | Startegy | Numeric | Boolean | Enum | Not periodic | Periodic | Linear interpolated | Keep-last-Value | Description |
|---|
| External | Reference to external data | | | | | | | | External data is converted to internal data and will be normalized and interpolated depending on the targeted time series. Example: meter readings, temperatures, switching states |
|---|
| Derivation of external data | |
|
|
| |
| | The derivation calculates the course growth of a source time series. Derivated, external data will be normalized and interpolated according to Keep-last-Value. Example: Calculation of the load profile from active energy | Reference
| Data point reference | | | | | | | | Data is copied from one data point to another and interpolated depending on the targeted time series. Example: Using the same value at different facilities (e.g. the outdoor temperature of a site for all corresponding buildings) |
|---|
Data point reference with differentiation | |
|
|
| |
| | The derivation calculates the course growth of a linear interpolated source time series. Derivated data will be normalized and interpolated according to Keep-last-Value. Example: Calculation of the load profile from active energy | | Data point reference with derivation(only positive values) | |
|
|
| |
| | The derivation calculates the course growth of a linear interpolated source time series. Derivated data will be normalized and interpolated according to Keep-last-Value. Negative values, that stem from a descending course of the source time series, are filtered out. This avoids distortions of results that could, for example, occur by meter exchanges. Example: Calculation of the load profile from meter readings. that can be resetted | | Data point reference with integration | |
|
|
| | |
| The integral calculates the area beneath a graph. In this case, data of a referenced Keep-Last-Value data points are integrated and and result in a linear interpolated time series. Example: Calculation of active energy from the load profile | | Child facilities | Average | |
|
|
| | | | With the help of this strategy, the data point receives values from ata points of subordinate facilities with the same meaning. The interpolation depends on the meaning and therefore stays the same. The average and sum are calculated with these values. In contrast to other strategies, sources are determined automatically and don't have to be chosen. Newly added, matching data points will be included immediately. Example: evaluating all load profiles of a site |
|---|
| Sum | |
|
|
| | | | | Script | Custom | | | |
| | | | Custom calculations can be created in QUDE with respective source time series. Those source time series stem from internal data points and properties. More information can be found here. |
|---|
| Value from logic class | Value from logic class | | | | | | | | This strategy was designed for special use cases. The values come from the facility itself. Their source depends on the respective case. Example: Site facilities |
|---|
| Manual value input | Manual value input | | | | | | | |
|
|---|
| 